TransportPCE Developer Guide¶
Overview¶
TransportPCE describes an application running on top of the OpenDaylight controller. Its primary function is to control an optical transport infrastructure using a non-proprietary South Bound Interface (SBI). It may be interconnected with Controllers of different layers (L2, L3 Controller…), a higher layer Controller and/or an Orchestrator through non-proprietary Application Programing Interfaces (APIs). Control includes the capability to configure the optical equipment, and to provision services according to a request coming from a higher layer controller and/or an orchestrator. This capability may rely on the controller only or it may be delegated to distributed (standardized) protocols.
Architecture¶
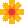
TransportPCE modular architecture is described on the next diagram. Each main function such as Topology management, Path Calculation Engine (PCE), Service handler, Renderer _responsible for the path configuration through optical equipment_ and Optical Line Management (OLM) is associated with a generic block relying on open models, each of them communicating through published APIs.
TransportPCE architecture¶
Fluorine, Neon and Sodium releases of transportPCE are dedicated to the control of WDM transport infrastructure. The WDM layer is built from colorless ROADMs and transponders.
The interest of using a controller to provision automatically services strongly relies on its ability to handle end to end optical services that span through the different network domains, potentially equipped with equipment coming from different suppliers. Thus, interoperability in the optical layer is a key element to get the benefit of automated control.
Initial design of TransportPCE leverages OpenROADM Multi-Source-Agreement (MSA) which defines interoperability specifications, consisting of both Optical interoperability and Yang data models.
End to end OTN services such as OCH-OTU4, structured ODU4 or 10GE-ODU2e services are supported since Magnesium SR2. OTN support continued to be improved in the following releases of Magnesium and Aluminium.
Flexgrid was introduced in Aluminium. Depending on OpenROADM device models, optical interfaces can be created according to the initial fixed grid (for R1.2.1, 96 channels regularly spaced of 50 GHz), or to a flexgrid (for R2.2.1 use of specific number of subsequent frequency slots of 6.25 GHz depending on one side of ROADMs and transponders capabilities and on the other side of the rate of the channel.
Leveraging Flexgrid feature, high rate services are supported since Silicon. First implementation allows rendering 400 GE services. This release also brings asynchronous service creation and deletion, thanks to northbound notifications modules based on a Kafka implementation, allowing interactions with the DMaaP Bus of ONAP.
Phosphorus consolidates end to end support for high rate services (ODUC4, OTUC4), allowing service creation and deletion from the NBI. The support of path computation for high rate services (OTUC4) has been added through the different P releases, relying on GNPy for impairment aware path computation. An experimental support of T-API is provided allowing service-create/delete from a T-API version 2.1.1 compliant NBI. A T-API network topology, with different levels of abstraction and service context are maintained in the MDSAL. Service state is managed, monitoring device port state changes. Associated notifications are handled through Kafka and DMaaP clients.
Sulfur is introducing OpenROADM service and network models 10.1, which include the operational-modes catalog, needed for future support of Alien Wavelength use cases. It also offers T-API notification support, handling the RPC associated with the notification subscription service.
The Chlorine release brings structural changes to the project. indeed, all the official yang models of the OpenROADM and ONF-TAPI communities are no longer managed directly in the TransportPCE project but in a dedicated sub-project: transportpce/models. Also, the implementation of these models which is made in TransportPCE now imports the models already compiled by maven dependency. From a functional point of view, Chlorine supports the autonomous reroute of WDM services terminated on 100G or 400G Transponders, as well as the beginning of developments around the OpenROAM catalog management.
The Argon release provides autonomous impairment aware path computation, relying on OpenROADM operational-modes catalog. It is used in a first step of the path validation, to evaluate the Optical Signal to Noise Ratio as well as the penalty associated with the signal across the calculated pass. Validation of the optical path by GNPy is still triggered, in a second step, leveraging advanced calculation of non linear contribution.
Module description¶
ServiceHandler¶
Service Handler handles request coming from a higher level controller or an orchestrator through the northbound API, as defined in the Open ROADM service model. Current implementation addresses the following rpcs: service-create, temp-service- create, service–delete, temp-service-delete, service-reroute, and service-restoration. It checks the request consistency and trigs path calculation sending rpcs to the PCE. If a valid path is returned by the PCE, path configuration is initiated relying on Renderer and OLM. At the confirmation of a successful service creation, the Service Handler updates the service-list/temp-service-list in the MD-SAL. For service deletion, the Service Handler relies on the Renderer and the OLM to delete connections and reset power levels associated with the service. The service-list is updated following a successful service deletion. In Neon SR0 is added the support for service from ROADM to ROADM, which brings additional flexibility and notably allows reserving resources when transponders are not in place at day one. Magnesium SR2 fully supports end-to-end OTN services which are part of the OTN infrastructure. It concerns the management of OCH-OTU4 (also part of the optical infrastructure) and structured HO-ODU4 services. Moreover, once these two kinds of OTN infrastructure service created, it is possible to manage some LO-ODU services (1GE-ODU0, 10GE-ODU2e). 100GE services are also supported over ODU4 in transponders or switchponders using higher rate network interfaces.
In Silicon release, the management of TopologyUpdateNotification coming from the Topology Management module was implemented. This functionality enables the controller to update the information of existing services according to the online status of the network infrastructure. If any service is affected by the topology update and the odl-transportpce-nbinotifications feature is installed, the Service Handler will send a notification to a Kafka server with the service update information.
PCE¶
The Path Computation Element (PCE) is the component responsible for path calculation. An interface allows the Service Handler or external components such as an orchestrator to request a path computation and get a response from the PCE including the computed path(s) in case of success, or errors and indication of the reason for the failure in case the request cannot be satisfied. Additional parameters can be provided by the PCE in addition to the computed paths if requested by the client module. An interface to the Topology Management module allows keeping PCE aligned with the latest changes in the topology. Information about current and planned services is available in the MD-SAL data store.
Current implementation of PCE allows finding the shortest path, minimizing either the hop count (default) or the propagation delay. The support of a flexible grid was introduced in Aluminium. The central wavelength assignment depends on the capabilities of the different devices on the path. If one of the elements only supports a fixed grid, the wavelength is assigned considering a grid of 96 wavelengths 50 GHz spaced. If all the devices on the path support a flexible grid, the assignment of wavelengths is done according to a flexible grid considering 768 subsequent slots of 6,25 GHz (total spectrum of 4.8 Thz).
The PCE module handles the following constraints as hard constraints:
Node exclusion
SRLG exclusion
Maximum latency
In Neon SR0, the PCE calculates the OSNR, on the base of incremental noise specifications provided in Open ROADM MSA. The support of unidirectional ports is also added. The interconnection of the PCE with GNPY (Gaussian Noise Python), an open-source library developed in the scope of the Telecom Infra Project for building route planning and optimizing performance in optical mesh networks, is supported since Magnesium SR0. This allowed introducing impairment aware path computation for (Beyond 100G) services across Phoshorus releases.
In Argon, we introduce autonomous impairment aware path computation, leveraging OpenROADM yang specification catalog (R10.1), which translates the optical specifications provided in the MSA into models understandable by the controller. To each disaggregated element crossed along the path (Transponders, ROADM add/drop modules and degrees), is associated an operational mode, for which each physical parameters is described in the catalog. This allows evaluating the degradations that each element, whether it is a device of fiber span, brings to the signal transmission. The resulting Optical Signal to Noise Ratio is calculated, as well as the penalties associated with the cumulated chromatic dispersion, Polarisation Mode Dispersion (PMD), Polarization Dependant Loss (PDL)… and the non-linear contribution is evaluated.
All of this is done in accordance with OpenROADM optical specifications. Handling OpenROADM specification catalogs improves the upgradability of the code, since the future evolution of the specifications only implies to add new operational modes to the catalog while the associated code remains unchanged.
In Argon SR0, to benefit from this new functionality, the specification catalog must be manually loaded into the data store. The catalog includes 2 different parts, the first being dedicated to the translation of OpenROADM specifications, the second (optional) being dedicated to specific operational modes for transponders used in “bookended” mode (same transponders on both ends of the path). The automatic filling of the first part of the catalog is planned in Ar SR1. In this release will also be supported the 2 RPCs used to fill the different parts of the catalog : - add-openroadm-operational-mode-to-catalog - add-specific-operational-mode-to-catalog
Autonomous impairment aware path computation is triggered in Argon for any path at the WDM layer, whatever is the service rate. The transmission margin is evaluated in both direction and the result is provided in INFO Logs. GNPy is used in a second step to enforce path validation. Indeed, it gives complementary information to the calculation made from OpenROADM specifications, with a finer assessment of non-linear contribution, and potentially a consideration of the interaction with other channels already provisioned on the network. This last capability will be added across Argon releases. The PCE forwards through a REST interface to GNPY external tool the topology and the pre-computed path translated in routing constraints. GNPy calculates a set of Quality of Transmission metrics for this path using its own library which includes models for OpenROADM. The result is sent back to the PCE. If the path is validated, the PCE sends back a response to the service handler. In case of invalidation of the path by GNPY, the PCE sends a new request to GNPY, including only the constraints expressed in the path-computation-request initiated by the Service Handler. GNPy then tries to calculate a path based on these relaxed constraints. The result of the path computation is provided to the PCE which translates the path according to the topology handled in transportPCE and forwards the results to the Service Handler.
GNPy relies on SNR and takes into account the linear and non-linear impairments to check feasibility. In the related tests, GNPy module runs externally in a docker and the communication with T-PCE is ensured via HTTPs.
Topology Management¶
Topology management module builds the Topology according to the Network model defined in OpenROADM. The topology is aligned with IETF I2RS RFC8345 model. It includes several network layers:
CLLI layer corresponds to the locations that host equipment
Network layer corresponds to a first level of disaggregation where we separate Xponders (transponder, muxponders or switchponders) from ROADMs
Topology layer introduces a second level of disaggregation where ROADMs Add/Drop modules (“SRGs”) are separated from the degrees which includes line amplifiers and WSS that switch wavelengths from one to another degree
OTN layer introduced in Magnesium includes transponders as well as switch-ponders and mux-ponders having the ability to switch OTN containers from client to line cards. Mg SR0 release includes creation of the switching pool (used to model cross-connect matrices), tributary-ports and tributary-slots at the initial connection of NETCONF devices. The population of OTN links (OTU4 and ODU4), and the adjustment of the tributary ports/slots pool occupancy when OTN services are created is supported since Magnesium SR2.
Since Silicon release, the Topology Management module process NETCONF event received through an event stream (as defined in RFC 5277) between devices and the NETCONF adapter of the controller. Current implementation detects device configuration changes and updates the topology datastore accordingly. Then, it sends a TopologyUpdateNotification to the Service Handler to indicate that a change has been detected in the network that may affect some of the already existing services.
Renderer¶
The Renderer module, on request coming from the Service Handler through a service- implementation-request /service delete rpc, sets/deletes the path corresponding to a specific service between A and Z ends. The path description provided by the service-handler to the renderer is based on abstracted resources (nodes, links and termination-points), as provided by the PCE module. The renderer converts this path-description in a path topology based on device resources (circuit-packs, ports,…).
The conversion from abstracted resources to device resources is performed relying on the portmapping module which maintains the connections between these different resource types. Portmapping module also allows to keep the topology independant from the devices releases. In Neon (SR0), portmapping module has been enriched to support both openroadm 1.2.1 and 2.2.1 device models. The full support of openroadm 2.2.1 device models (both in the topology management and the rendering function) has been added in Neon SR1. In Magnesium, portmapping is enriched with the supported-interface-capability, OTN supporting-interfaces, and switching-pools (reflecting cross-connection capabilities of OTN switch-ponders). The support for 7.1 devices models is introduced in Silicon (no devices of intermediate releases have been proposed and made available to the market by equipment manufacturers).
After the path is provided, the renderer first checks what are the existing interfaces on the ports of the different nodes that the path crosses. It then creates missing interfaces. After all needed interfaces have been created it sets the connections required in the nodes and notifies the Service Handler on the status of the path creation. Path is created in 2 steps (from A to Z and Z to A). In case the path between A and Z could not be fully created, a rollback function is called to set the equipment on the path back to their initial configuration (as they were before invoking the Renderer).
Magnesium brings the support of OTN services. SR0 supports the creation of OTU4, ODU4, ODU2/ODU2e and ODU0 interfaces. The creation of these low-order otn interfaces must be triggered through otn-service-path RPC. Magnesium SR2 fully supports end-to-end otn service implementation into devices (service-implementation-request /service delete rpc, topology alignement after the service has been created).
In Silicon releases, higher rate OTN interfaces (OTUC4) must be triggered through otn-service- path RPC. Phosphorus SR0 supports end-to-end otn service implementation into devices (service-implementation-request /service delete rpc, topology alignement after the service has been created). One shall note that impairment aware path calculation for higher rates will be made available across the Phosphorus release train.
OLM¶
Optical Line Management module implements two main features: it is responsible for setting up the optical power levels on the different interfaces, and is in charge of adjusting these settings across the life of the optical infrastructure.
After the different connections have been established in the ROADMS, between 2 Degrees for an express path, or between a SRG and a Degree for an Add or Drop path; meaning the devices have set WSS and all other required elements to provide path continuity, power setting are provided as attributes of these connections. This allows the device to set all complementary elements such as VOAs, to guaranty that the signal is launched at a correct power level (in accordance to the specifications) in the fiber span. This also applies to X-Ponders, as their output power must comply with the specifications defined for the Add/Drop ports (SRG) of the ROADM. OLM has the responsibility of calculating the right power settings, sending it to the device, and check the PM retrieved from the device to verify that the setting was correctly applied and the configuration was successfully completed.
Inventory¶
TransportPCE Inventory module is responsible to keep track of devices connected in an external MariaDB database. Other databases may be used as long as they comply with SQL and are compatible with OpenDaylight (for example MySQL). At present, the module supports extracting and persisting inventory of devices OpenROADM MSA version 1.2.1. Inventory module changes to support newer device models (2.2.1, etc) and other models (network, service, etc) will be progressively included.
The inventory module can be activated by the associated karaf feature (odl-transporpce-inventory) The database properties are supplied in the “opendaylight-release” and “opendaylight-snapshots” profiles. Below is the settings.xml with properties included in the distribution. The module can be rebuild from sources with different parameters.
Sample entry in settings.xml to declare an external inventory database:
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>opendaylight-release</id>
[..]
<properties>
<transportpce.db.host><<hostname>>:3306</transportpce.db.host>
<transportpce.db.database><<databasename>></transportpce.db.database>
<transportpce.db.username><<username>></transportpce.db.username>
<transportpce.db.password><<password>></transportpce.db.password>
<karaf.localFeature>odl-transportpce-inventory</karaf.localFeature>
</properties>
</profile>
[..]
<profile>
<id>opendaylight-snapshots</id>
[..]
<properties>
<transportpce.db.host><<hostname>>:3306</transportpce.db.host>
<transportpce.db.database><<databasename>></transportpce.db.database>
<transportpce.db.username><<username>></transportpce.db.username>
<transportpce.db.password><<password>></transportpce.db.password>
<karaf.localFeature>odl-transportpce-inventory</karaf.localFeature>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
Once the project built and when karaf is started, the cfg file is generated in etc folder with the corresponding properties supplied in settings.xml. When devices with OpenROADM 1.2.1 device model are mounted, the device listener in the inventory module loads several device attributes to various tables as per the supplied database. The database structure details can be retrieved from the file tests/inventory/initdb.sql inside project sources. Installation scripts and a docker file are also provided.
Key APIs and Interfaces¶
External API¶
North API, interconnecting the Service Handler to higher level applications relies on the Service Model defined in the MSA. The Renderer and the OLM are developed to allow configuring OpenROADM devices through a southbound Netconf/Yang interface and rely on the MSA’s device model.
ServiceHandler Service¶
RPC call
service-create (given service-name, service-aend, service-zend)
service-delete (given service-name)
service-reroute (given service-name, service-aend, service-zend)
service-restoration (given service-name, service-aend, service-zend)
temp-service-create (given common-id, service-aend, service-zend)
temp-service-delete (given common-id)
Data structure
service list : made of services
temp-service list : made of temporary services
service : composed of service-name, topology wich describes the detailed path (list of used resources)
Notification
service-rpc-result : result of service RPC
service-notification : service has been added, modified or removed
Netconf Service¶
RPC call
connect-device : PUT
disconnect-device : DELETE
check-connected-device : GET
Data Structure
node list : composed of netconf nodes in topology-netconf
Internal APIs¶
Internal APIs define REST APIs to interconnect TransportPCE modules :
Service Handler to PCE
PCE to Topology Management
Service Handler to Renderer
Renderer to OLM
Network Model to Service Handler
Pce Service¶
RPC call
path-computation-request (given service-name, service-aend, service-zend)
cancel-resource-reserve (given service-name)
Notification
service-path-rpc-result : result of service RPC
Renderer Service¶
RPC call
service-implementation-request (given service-name, service-aend, service-zend)
service-delete (given service-name)
Data structure
service path list : composed of service paths
service path : composed of service-name, path description giving the list of abstracted elements (nodes, tps, links)
Notification
service-path-rpc-result : result of service RPC
Device Renderer¶
RPC call
service-path used in SR0 as an intermediate solution to address directly the renderer from a REST NBI to create OCH-OTU4-ODU4 interfaces on network port of otn devices.
otn-service-path used in SR0 as an intermediate solution to address directly the renderer from a REST NBI for otn-service creation. Otn service-creation through service-implementation-request call from the Service Handler will be supported in later Magnesium releases
Topology Management Service¶
Data structure
network list : composed of networks(openroadm-topology, netconf-topology)
node list : composed of nodes identified by their node-id
link list : composed of links identified by their link-id
node : composed of roadm, xponder link : composed of links of different types (roadm-to-roadm, express, add-drop …)
OLM Service¶
RPC call
get-pm (given node-id)
service-power-setup
service-power-turndown
service-power-reset
calculate-spanloss-base
calculate-spanloss-current
odl-transportpce-stubmodels¶
This feature provides function to be able to stub some of TransportPCE modules, pce and renderer (Stubpce and Stubrenderer). Stubs are used for development purposes and can be used for some of the functional tests.
Interfaces to external software¶
It defines the interfaces implemented to interconnect TransportPCE modules with other software in order to perform specific tasks
GNPy interface¶
Request structure
topology : composed of list of elements and connections
service : source, destination, explicit-route-objects, path-constraints
Response structure
path-properties/path-metric : OSNR-0.1nm, OSNR-bandwidth, SNR-0.1nm, SNR-bandwidth,
path-properties/path-route-objects : composed of path elements
Running transportPCE project¶
To use transportPCE controller, the first step is to connect the controller to optical nodes through the NETCONF connector.
Note
In the current version, only optical equipment compliant with open ROADM datamodels are managed by transportPCE.
Since Chlorine release, the bierman implementation of RESTCONF is no longer supported for the benefit of the RFC8040. Thus REST API must be compliant to the RFC8040 format.
Connecting nodes¶
To connect a node, use the following RESTconf request
REST API : PUT /rests/data/network-topology:network-topology/topology=topology-netconf/node=<node-id>
Sample JSON Data
{
"node": [
{
"node-id": "<node-id>",
"netconf-node-topology:tcp-only": "false",
"netconf-node-topology:reconnect-on-changed-schema": "false",
"netconf-node-topology:host": "<node-ip-address>",
"netconf-node-topology:default-request-timeout-millis": "120000",
"netconf-node-topology:max-connection-attempts": "0",
"netconf-node-topology:sleep-factor": "1.5",
"netconf-node-topology:actor-response-wait-time": "5",
"netconf-node-topology:concurrent-rpc-limit": "0",
"netconf-node-topology:between-attempts-timeout-millis": "2000",
"netconf-node-topology:port": "<netconf-port>",
"netconf-node-topology:connection-timeout-millis": "20000",
"netconf-node-topology:username": "<node-username>",
"netconf-node-topology:password": "<node-password>",
"netconf-node-topology:keepalive-delay": "300"
}
]
}
Then check that the netconf session has been correctly established between the controller and the node. the status of netconf-node-topology:connection-status must be connected
REST API : GET /rests/data/network-topology:network-topology/topology=topology-netconf/node=<node-id>?content=nonconfig
Node configuration discovery¶
Once the controller is connected to the node, transportPCE application automatically launchs a discovery of the node configuration datastore and creates Logical Connection Points to any physical ports related to transmission. All circuit-packs inside the node configuration are analyzed.
Use the following RESTconf URI to check that function internally named portMapping.
REST API : GET /rests/data/transportpce-portmapping:network
Note
- In
org-openroadm-device.yang, four types of optical nodes can be managed: rdm: ROADM device (optical switch)
xpdr: Xponder device (device that converts client to optical channel interface)
ila: in line amplifier (optical amplifier)
extplug: external pluggable (an optical pluggable that can be inserted in an external unit such as a router)
TransportPCE currently supports rdm and xpdr
Depending on the kind of open ROADM device connected, different kind of Logical Connection Points should appear, if the node configuration is not empty:
DEG<degree-number>-TTP-<port-direction>: created on the line port of a degree on a rdm equipment
SRG<srg-number>-PP<port-number>: created on the client port of a srg on a rdm equipment
XPDR<number>-CLIENT<port-number>: created on the client port of a xpdr equipment
XPDR<number>-NETWORK<port-number>: created on the line port of a xpdr equipment
For further details on openROADM device models, see openROADM MSA white paper.
Optical Network topology¶
Before creating an optical connectivity service, your topology must contain at least two xpdr devices connected to two different rdm devices. Normally, the openroadm-topology is automatically created by transportPCE. Nevertheless, depending on the configuration inside optical nodes, this topology can be partial. Check that link of type ROADMtoROADM exists between two adjacent rdm nodes.
REST API : GET /rests/data/ietf-network:networks/network=openroadm-topology
If it is not the case, you need to manually complement the topology with ROADMtoROADM link using the following REST RPC:
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-networkutils:init-roadm-nodes
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"rdm-a-node": "<node-id-A>",
"deg-a-num": "<degree-A-number>",
"termination-point-a": "<Logical-Connection-Point>",
"rdm-z-node": "<node-id-Z>",
"deg-z-num": "<degree-Z-number>",
"termination-point-z": "<Logical-Connection-Point>"
}
}
<Logical-Connection-Point> comes from the portMapping function.
Unidirectional links between xpdr and rdm nodes must be created manually. To that end use the two following REST RPCs:
From xpdr to rdm:¶
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-networkutils:init-xpdr-rdm-links
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"links-input": {
"xpdr-node": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"xpdr-num": "1",
"network-num": "<xpdr-network-port-number>",
"rdm-node": "<rdm-node-id>",
"srg-num": "<srg-number>",
"termination-point-num": "<Logical-Connection-Point>"
}
}
}
From rdm to xpdr:¶
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-networkutils:init-rdm-xpdr-links
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"links-input": {
"xpdr-node": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"xpdr-num": "1",
"network-num": "<xpdr-network-port-number>",
"rdm-node": "<rdm-node-id>",
"srg-num": "<srg-number>",
"termination-point-num": "<Logical-Connection-Point>"
}
}
}
OTN topology¶
Before creating an OTN service, your topology must contain at least two xpdr devices of MUXPDR or SWITCH type connected to two different rdm devices. To check that these xpdr are present in the OTN topology, use the following command on the REST API :
REST API : GET /rests/data/ietf-network:networks/network=otn-topology
An optical connectivity service shall have been created in a first setp. Since Magnesium SR2, the OTN links are automatically populated in the topology after the Och, OTU4 and ODU4 interfaces have been created on the two network ports of the xpdr.
Creating a service¶
Use the service handler module to create any end-to-end connectivity service on an OpenROADM network. Two different kinds of end-to-end “optical” services are managed by TransportPCE: - 100GE/400GE services from client port to client port of two transponders (TPDR) - Optical Channel (OC) service from client add/drop port (PP port of SRG) to client add/drop port of two ROADMs.
For these services, TransportPCE automatically invokes renderer module to create all required interfaces and cross-connection on each device supporting the service. As an example, the creation of a 100GE service implies among other things, the creation of OCH or Optical Tributary Signal (OTSi), OTU4 and ODU4 interfaces on the Network port of TPDR devices. The creation of a 400GE service implies the creation of OTSi, OTUC4, ODUC4 and ODU4 interfaces on the Network port of TPDR devices.
Since Magnesium SR2, the service handler module directly manages some end-to-end otn connectivity services. Before creating a low-order OTN service (1GE or 10GE services terminating on client port of MUXPDR or SWITCH), the user must ensure that a high-order ODU4 container exists and has previously been configured (it means structured to support low-order otn services) to support low-order OTN containers. Thus, OTN service creation implies three steps: 1. OCH-OTU4 service from network port to network port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH) 2. HO-ODU4 service from network port to network port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH) 3. 10GE service creation from client port to client port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH)
The management of other OTN services (1GE-ODU0, 100GE…) is planned for future releases.
100GE service creation¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create a bidirectional end-to-end optical connectivity service between two xpdr over an optical network composed of rdm nodes.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-create
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-create",
"request-system-id": "appname"
},
"service-name": "test1",
"common-id": "commonId",
"connection-type": "service",
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "Ethernet",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "Ethernet",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"due-date": "yyyy-mm-ddT00:00:01Z",
"operator-contact": "some-contact-info"
}
}
Most important parameters for this REST RPC are the identification of the two physical client ports on xpdr nodes.This RPC invokes the PCE module to compute a path over the openroadm-topology and then invokes renderer and OLM to implement the end-to-end path into the devices.
OC service creation¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create a bidirectional end-to end Optical Channel (OC) connectivity service between two add/drop ports (PP port of SRG node) over an optical network only composed of rdm nodes.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-create
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-create",
"request-system-id": "appname"
},
"service-name": "something",
"common-id": "commonId",
"connection-type": "roadm-line",
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "OC",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "OC",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-client-port>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-number>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"due-date": "yyyy-mm-ddT00:00:01Z",
"operator-contact": "some-contact-info"
}
}
As for the previous RPC, this RPC invokes the PCE module to compute a path over the openroadm-topology and then invokes renderer and OLM to implement the end-to-end path into the devices.
OTN OCH-OTU4 service creation¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create over the optical infrastructure a bidirectional end-to-end OTU4 over an optical wavelength connectivity service between two optical network ports of OTN Xponder (MUXPDR or SWITCH). Such service configure the optical network infrastructure composed of rdm nodes.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-create
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-create",
"request-system-id": "appname"
},
"service-name": "something",
"common-id": "commonId",
"connection-type": "infrastructure",
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "OTU",
"otu-service-rate": "org-openroadm-otn-common-types:OTU4",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "OTU",
"otu-service-rate": "org-openroadm-otn-common-types:OTU4",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"due-date": "yyyy-mm-ddT00:00:01Z",
"operator-contact": "some-contact-info"
}
}
As for the previous RPC, this RPC invokes the PCE module to compute a path over the openroadm-topology and then invokes renderer and OLM to implement the end-to-end path into the devices.
OTSi-OTUC4 service creation¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create over the optical infrastructure a bidirectional end-to-end OTUC4 over an optical Optical Tributary Signal connectivity service between two optical network ports of OTN Xponder (MUXPDR or SWITCH). Such service configure the optical network infrastructure composed of rdm nodes.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-create
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-create",
"request-system-id": "appname"
},
"service-name": "something",
"common-id": "commonId",
"connection-type": "infrastructure",
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "400",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "OTU",
"otu-service-rate": "org-openroadm-otn-common-types:OTUCn",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "400",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "OTU",
"otu-service-rate": "org-openroadm-otn-common-types:OTUCn",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"due-date": "yyyy-mm-ddT00:00:01Z",
"operator-contact": "some-contact-info"
}
}
As for the previous RPC, this RPC invokes the PCE module to compute a path over the openroadm-topology and then invokes renderer and OLM to implement the end-to-end path into the devices.
One shall note that in Phosphorus SR0, as the OpenROADM 400G specification are not available (neither in the GNPy libraries, nor in the PCE module), path validation will be performed using the same asumptions as we use for 100G. This means the path may be validated whereas optical performances do not reach expected levels. This allows testing OpenROADM device implementing B100G rates, but shall not be used in operational conditions. The support for higher rate impairment aware path computation will be introduced across Phosphorus release train.
ODUC4 service creation¶
For ODUC4 service creation, the REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create an ODUC4 over the OTSi-OTUC4 has the same format as the RPC used for the creation of this last. Only “service-format” needs to be changed to “ODU”, and “otu-service-rate” : “org-openroadm-otn-common- types:OTUCn” needs to be replaced by: “odu-service-rate” : “org-openroadm-otn-common-types:ODUCn” in both service-a-end and service-z-end containers.
OTN HO-ODU4 service creation¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create over the optical infrastructure a bidirectional end-to-end ODU4 OTN service over an OTU4 and structured to support low-order OTN services (ODU2e, ODU0). As for OTU4, such a service must be created between two network ports of OTN Xponder (MUXPDR or SWITCH).
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-create
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-create",
"request-system-id": "appname"
},
"service-name": "something",
"common-id": "commonId",
"connection-type": "infrastructure",
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "ODU",
"otu-service-rate": "org-openroadm-otn-common-types:ODU4",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "ODU",
"otu-service-rate": "org-openroadm-otn-common-types:ODU4",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-network-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"due-date": "yyyy-mm-ddT00:00:01Z",
"operator-contact": "some-contact-info"
}
}
As for the previous RPC, this RPC invokes the PCE module to compute a path over the otn-topology that must contains OTU4 links with valid bandwidth parameters, and then invokes renderer and OLM to implement the end-to-end path into the devices.
OTN 10GE-ODU2e service creation¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to create over the OTN infrastructure a bidirectional end-to-end 10GE-ODU2e OTN service over an ODU4. Such a service must be created between two client ports of OTN Xponder (MUXPDR or SWITCH) configured to support 10GE interfaces.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-create
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-create",
"request-system-id": "appname"
},
"service-name": "something",
"common-id": "commonId",
"connection-type": "service",
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "10",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "Ethernet",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"subrate-eth-sla": {
"subrate-eth-sla": {
"committed-info-rate": "10000",
"committed-burst-size": "64"
}
},
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "10",
"node-id": "<xpdr-node-id>",
"service-format": "Ethernet",
"clli": "<ccli-name>",
"subrate-eth-sla": {
"subrate-eth-sla": {
"committed-info-rate": "10000",
"committed-burst-size": "64"
}
},
"tx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"rx-direction": [{
"port": {
"port-device-name": "<xpdr-node-id-in-otn-topology>",
"port-type": "fixed",
"port-name": "<xpdr-client-port-in-otn-topology>",
"port-rack": "000000.00",
"port-shelf": "Chassis#1"
},
"lgx": {
"lgx-device-name": "Some lgx-device-name",
"lgx-port-name": "Some lgx-port-name",
"lgx-port-rack": "000000.00",
"lgx-port-shelf": "00"
},
"index": 0
}],
"optic-type": "gray"
},
"due-date": "yyyy-mm-ddT00:00:01Z",
"operator-contact": "some-contact-info"
}
}
As for the previous RPC, this RPC invokes the PCE module to compute a path over the otn-topology that must contains ODU4 links with valid bandwidth parameters, and then invokes renderer and OLM to implement the end-to-end path into the devices.
Note
Since Magnesium SR2, the service-list corresponding to OCH-OTU4, ODU4 or again 10GE-ODU2e services is updated in the service-list datastore.
Note
trib-slot is used when the equipment supports contiguous trib-slot allocation (supported from Magnesium SR0). The trib-slot provided corresponds to the first of the used trib-slots. complex-trib-slots will be used when the equipment does not support contiguous trib-slot allocation. In this case a list of the different trib-slots to be used shall be provided. The support for non contiguous trib-slot allocation is planned for later release.
Deleting a service¶
Deleting any kind of service¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke service handler module in order to delete a given optical connectivity service.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/org-openroadm-service:service-delete
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"sdnc-request-header": {
"request-id": "request-1",
"rpc-action": "service-delete",
"request-system-id": "appname",
"notification-url": "http://localhost:8585/NotificationServer/notify"
},
"service-delete-req-info": {
"service-name": "something",
"tail-retention": "no"
}
}
}
Most important parameters for this REST RPC is the service-name.
Note
Deleting OTN services implies proceeding in the reverse way to their creation. Thus, OTN service deletion must respect the three following steps: 1. delete first all 10GE services supported over any ODU4 to be deleted 2. delete ODU4 3. delete OCH-OTU4 supporting the just deleted ODU4
Invoking PCE module¶
Use the following REST RPCs to invoke PCE module in order to check connectivity between xponder nodes and the availability of a supporting optical connectivity between the network-ports of the nodes.
Checking OTU4 service connectivity¶
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-pce:path-computation-request
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"service-name": "something",
"resource-reserve": "true",
"service-handler-header": {
"request-id": "request1"
},
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"clli": "<clli-node>",
"service-format": "OTU",
"node-id": "<otn-node-id>"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"clli": "<clli-node>",
"service-format": "OTU",
"node-id": "<otn-node-id>"
},
"pce-routing-metric": "hop-count"
}
}
Note
here, the <otn-node-id> corresponds to the node-id as appearing in “openroadm-network” topology layer
Checking ODU4 service connectivity¶
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-pce:path-computation-request
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"service-name": "something",
"resource-reserve": "true",
"service-handler-header": {
"request-id": "request1"
},
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"clli": "<clli-node>",
"service-format": "ODU",
"node-id": "<otn-node-id>"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "100",
"clli": "<clli-node>",
"service-format": "ODU",
"node-id": "<otn-node-id>"
},
"pce-routing-metric": "hop-count"
}
}
Note
here, the <otn-node-id> corresponds to the node-id as appearing in “otn-topology” layer
Checking 10GE/ODU2e service connectivity¶
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-pce:path-computation-request
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"service-name": "something",
"resource-reserve": "true",
"service-handler-header": {
"request-id": "request1"
},
"service-a-end": {
"service-rate": "10",
"clli": "<clli-node>",
"service-format": "Ethernet",
"node-id": "<otn-node-id>"
},
"service-z-end": {
"service-rate": "10",
"clli": "<clli-node>",
"service-format": "Ethernet",
"node-id": "<otn-node-id>"
},
"pce-routing-metric": "hop-count"
}
}
Note
here, the <otn-node-id> corresponds to the node-id as appearing in “otn-topology” layer
odl-transportpce-tapi¶
This feature allows TransportPCE application to expose at its northbound interface other APIs than those defined by the OpenROADM MSA. With this feature, TransportPCE provides part of the Transport-API specified by the Open Networking Foundation. More specifically, the Topology Service, Connectivity and Notification Service components are implemented, allowing to:
Expose to higher level applications an abstraction of its OpenROADM topologies in the form of topologies respecting the T-API modelling.
Create/delete connectivity services between the Service Interface Points (SIPs) exposed by the T-API topology.
Create/Delete Notification Subscription Service to expose to higher level applications T-API notifications through a Kafka server.
The current version of TransportPCE implements the tapi-topology.yang, tapi-connectivity.yang and tapi-notification.yang models in the revision 2018-12-10 (T-API v2.1.2).
Additionally, support for the Path Computation Service will be added in future releases, which will allow T-PCE to compute a path over the T-API topology.
T-API Topology Service¶
RPC calls implemented:
get-topology-details
get-node-details
get-node-edge-point-details
get-link-details
get-topology-list
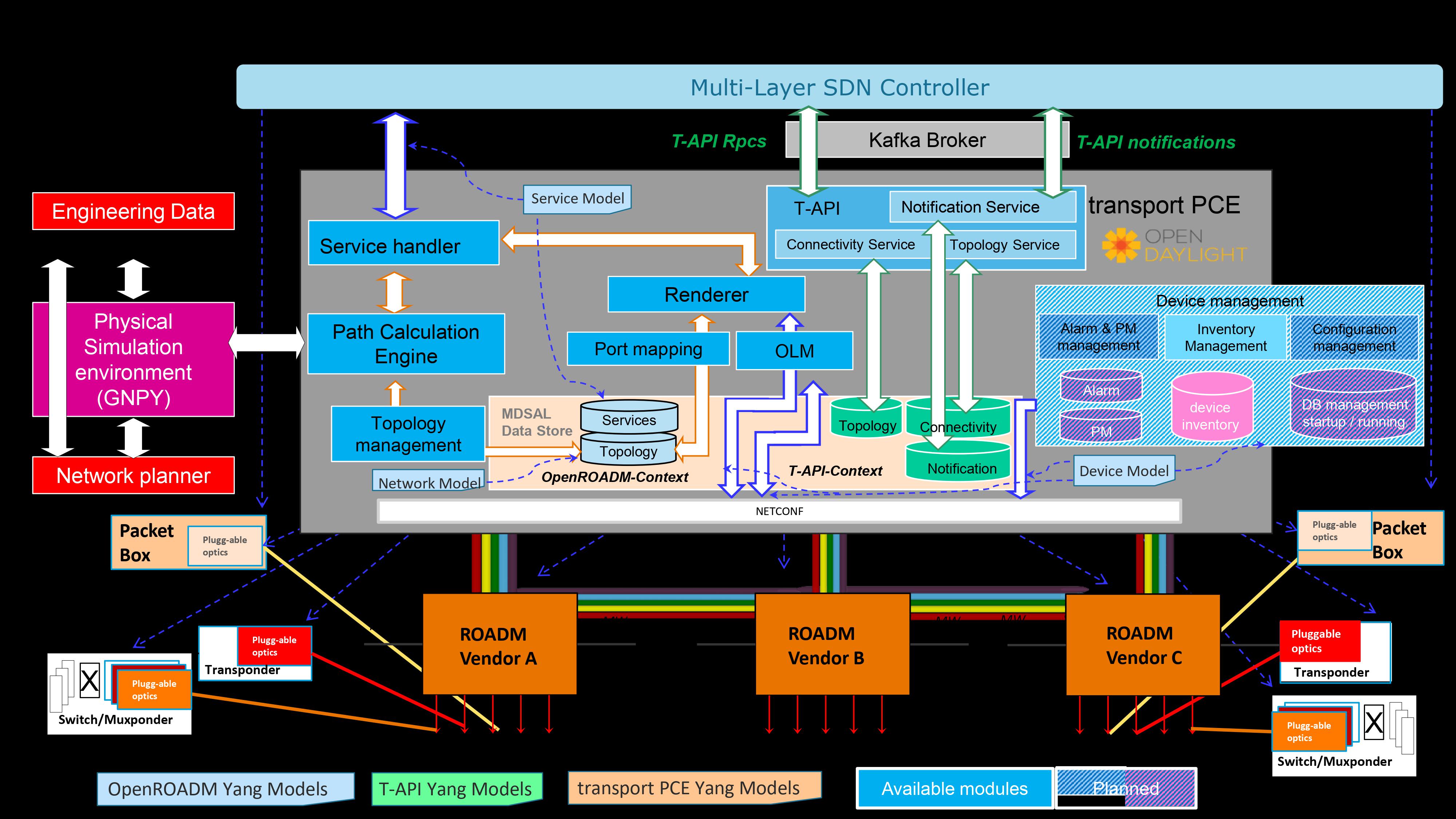
As in IETF or OpenROADM topologies, T-API topologies are composed of lists of nodes and links that abstract a set of network resources. T-API specifies the T0 - Multi-layer topology which is, as indicated by its name, a single topology that collapses network logical abstraction for all network layers. Thus, an OpenROADM device as, for example, an OTN xponder that manages the following network layers ETH, ODU, OTU, Optical wavelength, will be represented in T-API T0 topology by two nodes: one DSR/ODU node and one Photonic Media node. Each of them are linked together through one or several transitional links depending on the number of network/line ports on the device.
Aluminium SR2 comes with a complete refactoring of this module, handling the same way multi-layer abstraction of any Xponder terminal device, whether it is a 100G transponder, an OTN muxponder or again an OTN switch. For all these devices, the implementation manages the fact that only relevant ports must appear in the resulting TAPI topology abstraction. In other words, only client/network ports that are undirectly/directly connected to the ROADM infrastructure are considered for the abstraction. Moreover, the whole ROADM infrastructure of the network is also abstracted towards a single photonic node. Therefore, a pair of unidirectional xponder-output/xponder-input links present in openroadm-topology is represented by a bidirectional OMS link in TAPI topology. In the same way, a pair of unidirectional OTN links (OTU4, ODU4) present in otn-topology is also represented by a bidirectional OTN link in TAPI topology, while retaining their available bandwidth characteristics.
Phosphorus SR0 extends the T-API topology service implementation by bringing a fully described topology. T0 - Full Multi-layer topology is derived from the existing T0 - Multi-layer topology. But the ROADM infrastructure is not abstracted and the higher level application can get more details on the composition of the ROADM infrastructure controlled by TransportPCE. Each ROADM node found in the openroadm-network is converted into a Photonic Media node. The details of these T-API nodes are obtained from the openroadm-topology. Therefore, the external traffic ports of Degree and SRG nodes are represented with a set of Network Edge Points (NEPs) and SIPs belonging to the Photonic Media node and a pair of roadm-to-roadm links present in openroadm-topology is represented by a bidirectional OMS link in TAPI topology. Additionally, T-API topology related information is stored in TransportPCE datastore in the same way as OpenROADM topology layers. When a node is connected to the controller through the corresponding REST API, the T-API topology context gets updated dynamically and stored.
Note
A naming nomenclature is defined to be able to map T-API and OpenROADM data. i.e., T-API_roadm_Name = OpenROADM_roadmID+T-API_layer i.e., T-API_roadm_nep_Name = OpenROADM_roadmID+T-API_layer+OpenROADM_terminationPointID
Three kinds of topologies are currently implemented. The first one is the “T0 - Multi-layer topology” defined in the reference implementation of T-API. This topology gives an abstraction from data coming from openroadm-topology and otn-topology. Such topology may be rather complex since most of devices are represented through several nodes and links. Another topology, named “Transponder 100GE”, is also implemented. That latter provides a higher level of abstraction, much simpler, for the specific case of 100GE transponder, in the form of a single DSR node. Lastly, the T0 - Full Multi-layer topology topology was added. This topology collapses the data coming from openroadm-network, openroadm-topology and otn-topology. It gives a complete view of the optical network as defined in the reference implementation of T-API
The figure below shows an example of TAPI abstractions as performed by TransportPCE starting from Aluminium SR2.
In this specific case, as far as the “A” side is concerned, we connect TransportPCE to two xponder terminal devices at the netconf level : - XPDR-A1 is a 100GE transponder and is represented by XPDR-A1-XPDR1 node in otn-topology - SPDR-SA1 is an otn xponder that actually contains in its device configuration datastore two otn xponder nodes (the otn muxponder 10GE=>100G SPDR-SA1-XPDR1 and the otn switch 4x100GE => 4x100G SPDR-SA1-XPDR2) As represented on the bottom part of the figure, only one network port of XPDR-A1-XPDR1 is connected to the ROADM infrastructure, and only one network port of the otn muxponder is also attached to the ROADM infrastructure. Such network configuration will result in the TAPI T0 - Multi-layer topology abstraction as represented in the center of the figure. Let’s notice that the otn switch (SPDR-SA1-XPDR2), not being attached to the ROADM infrastructure, is not abstracted. Moreover, 100GE transponder being connected, the TAPI Transponder 100GE topology will result in a single layer DSR node with only the two Owned Node Edge Ports representing the two 100GE client ports of respectively XPDR-A1-XPDR1 and XPDR-C1-XPDR1…
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-topology:get-topology-details
This request builds the TAPI T0 - Multi-layer topology abstraction with regard to the current state of openroadm-topology and otn-topology topologies stored in OpenDaylight datastores.
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-topology:input": {
"tapi-topology:topology-id-or-name": "T0 - Multi-layer topology"
}
}
This request builds the TAPI Transponder 100GE abstraction with regard to the current state of openroadm-topology and otn-topology topologies stored in OpenDaylight datastores. Its main interest is to simply and directly retrieve 100GE client ports of 100G Transponders that may be connected together, through a point-to-point 100GE service running over a wavelength.
{
"tapi-topology:input": {
"tapi-topology:topology-id-or-name": "Transponder 100GE"
}
}
Note
As for the T0 multi-layer topology, only 100GE client port whose their associated 100G line port is connected to Add/Drop nodes of the ROADM infrastructure are retrieved in order to abstract only relevant information.
This request builds the TAPI T0 - Full Multi-layer topology with respect to the information existing in the T-API topology context stored in OpenDaylight datastores.
{
"tapi-topology:input": {
"tapi-topology:topology-id-or-name": "T0 - Full Multi-layer topology"
}
}
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-topology:get-node-details
This request returns the information, stored in the Topology Context, of the corresponding T-API node. The user can provide, either the Uuid associated to the attribute or its name.
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-topology:input": {
"tapi-topology:topology-id-or-name": "T0 - Full Multi-layer topology",
"tapi-topology:node-id-or-name": "ROADM-A1+PHOTONIC_MEDIA"
}
}
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-topology:get-node-edge-point-details
This request returns the information, stored in the Topology Context, of the corresponding T-API NEP. The user can provide, either the Uuid associated to the attribute or its name.
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-topology:input": {
"tapi-topology:topology-id-or-name": "T0 - Full Multi-layer topology",
"tapi-topology:node-id-or-name": "ROADM-A1+PHOTONIC_MEDIA",
"tapi-topology:ep-id-or-name": "ROADM-A1+PHOTONIC_MEDIA+DEG1-TTP-TXRX"
}
}
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-topology:get-link-details
This request returns the information, stored in the Topology Context, of the corresponding T-API link. The user can provide, either the Uuid associated to the attribute or its name.
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-topology:input": {
"tapi-topology:topology-id-or-name": "T0 - Full Multi-layer topology",
"tapi-topology:link-id-or-name": "ROADM-C1-DEG1-DEG1-TTP-TXRXtoROADM-A1-DEG2-DEG2-TTP-TXRX"
}
}
T-API Connectivity & Common Services¶
Phosphorus SR0 extends the T-API interface support by implementing the T-API connectivity Service. This interface enables a higher level controller or an orchestrator to request the creation of connectivity services as defined in the tapi-connectivity model. As it is necessary to indicate the two (or more) SIPs (or endpoints) of the connectivity service, the tapi-common model is implemented to retrieve from the datastore all the innformation related to the SIPs in the tapi-context. Current implementation of the connectivity service maps the connectivity-request into the appropriate openroadm-service-create and relies on the Service Handler to perform path calculation and configuration of devices. Results received from the PCE and the Rendererare mapped back into T-API to create the corresponding Connection End Points (CEPs) and Connections in the T-API Connectivity Context and store it in the datastore.
This first implementation includes the creation of:
ROADM-to-ROADM tapi-connectivity service (MC connectivity service)
OTN tapi-connectivity services (OCh/OTU, OTSi/OTU & ODU connectivity services)
Ethernet tapi-connectivity services (DSR connectivity service)
RPC calls implemented
create-connectivity-service
get-connectivity-service-details
get-connection-details
delete-connectivity-service
get-connection-end-point-details
get-connectivity-service-list
get-service-interface-point-details
get-service-interface-point-list
Creating a T-API Connectivity service¶
Use the tapi interface to create any end-to-end connectivity service on a T-API based network. Two kind of end-to-end “optical” connectivity services are managed by TransportPCE T-API module: - 10GE service from client port to client port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH) - Media Channel (MC) connectivity service from client add/drop port (PP port of SRG) to client add/drop port of two ROADMs.
As mentioned earlier, T-API module interfaces with the Service Handler to automatically invoke the renderer module to create all required tapi connections and cross-connection on each device supporting the service.
Before creating a low-order OTN connectivity service (1GE or 10GE services terminating on client port of MUXPDR or SWITCH), the user must ensure that a high-order ODU4 container exists and has previously been configured (it means structured to support low-order otn services) to support low-order OTN containers.
Thus, OTN connectivity service creation implies three steps: 1. OTSi/OTU connectivity service from network port to network port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH in Photonic media layer) 2. ODU connectivity service from network port to network port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH in DSR/ODU layer) 3. 10GE connectivity service creation from client port to client port of two OTN Xponders (MUXPDR or SWITCH in DSR/ODU layer)
The first step corresponds to the OCH-OTU4 service from network port to network port of OpenROADM. The corresponding T-API cross and top connections are created between the CEPs of the T-API nodes involved in each request.
Additionally, an MC connectivity service could be created between two ROADMs to create an optical tunnel and reserve resources in advance. This kind of service corresponds to the OC service creation use case described earlier.
The management of other OTN services through T-API (1GE-ODU0, 100GE…) is planned for future releases.
Any-Connectivity service creation¶
As for the Service Creation described for OpenROADM, the initial steps are the same:
Connect netconf devices to the controller
Create XPDR-RDM links and configure RDM-to-RDM links (in openroadm topologies)
Bidirectional T-API links between xpdr and rdm nodes must be created manually. To that end, use the following REST RPCs:
From xpdr <–> rdm:¶
REST API : POST /rests/operations/transportpce-tapinetworkutils:init-xpdr-rdm-tapi-link
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"xpdr-node": "<XPDR_OpenROADM_id>",
"network-tp": "<XPDR_TP_OpenROADM_id>",
"rdm-node": "<ROADM_OpenROADM_id>",
"add-drop-tp": "<ROADM_TP_OpenROADM_id>"
}
}
Use the following REST RPC to invoke T-API module in order to create a bidirectional connectivity service between two devices. The network should be composed of two ROADMs and two Xponders (SWITCH or MUX)
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-connectivity:create-connectivity-service
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-connectivity:input": {
"tapi-connectivity:end-point": [
{
"tapi-connectivity:layer-protocol-name": "<Node_TAPI_Layer>",
"tapi-connectivity:service-interface-point": {
"tapi-connectivity:service-interface-point-uuid": "<SIP_UUID_of_NEP>"
},
"tapi-connectivity:administrative-state": "UNLOCKED",
"tapi-connectivity:operational-state": "ENABLED",
"tapi-connectivity:direction": "BIDIRECTIONAL",
"tapi-connectivity:role": "SYMMETRIC",
"tapi-connectivity:protection-role": "WORK",
"tapi-connectivity:local-id": "<OpenROADM node ID>",
"tapi-connectivity:name": [
{
"tapi-connectivity:value-name": "OpenROADM node id",
"tapi-connectivity:value": "<OpenROADM node ID>"
}
]
},
{
"tapi-connectivity:layer-protocol-name": "<Node_TAPI_Layer>",
"tapi-connectivity:service-interface-point": {
"tapi-connectivity:service-interface-point-uuid": "<SIP_UUID_of_NEP>"
},
"tapi-connectivity:administrative-state": "UNLOCKED",
"tapi-connectivity:operational-state": "ENABLED",
"tapi-connectivity:direction": "BIDIRECTIONAL",
"tapi-connectivity:role": "SYMMETRIC",
"tapi-connectivity:protection-role": "WORK",
"tapi-connectivity:local-id": "<OpenROADM node ID>",
"tapi-connectivity:name": [
{
"tapi-connectivity:value-name": "OpenROADM node id",
"tapi-connectivity:value": "<OpenROADM node ID>"
}
]
}
],
"tapi-connectivity:connectivity-constraint": {
"tapi-connectivity:service-layer": "<TAPI_Service_Layer>",
"tapi-connectivity:service-type": "POINT_TO_POINT_CONNECTIVITY",
"tapi-connectivity:service-level": "Some service-level",
"tapi-connectivity:requested-capacity": {
"tapi-connectivity:total-size": {
"value": "<CAPACITY>",
"unit": "GB"
}
}
},
"tapi-connectivity:state": "Some state"
}
}
As for the previous RPC, MC and OTSi correspond to PHOTONIC_MEDIA layer services, ODU to ODU layer services and 10GE/DSR to DSR layer services. This RPC invokes the Service Handler module to trigger the PCE to compute a path over the otn-topology that must contains ODU4 links with valid bandwidth parameters. Once the path is computed and validated, the T-API CEPs (associated with a NEP), cross connections and top connections will be created according to the service request and the topology objects inside the computed path. Then, the renderer and OLM are invoked to implement the end-to-end path into the devices and to update the status of the connections and connectivity service.
Note
Refer to the “Unconstrained E2E Service Provisioning” use cases from T-API Reference Implementation to get more details about the process of connectivity service creation
Deleting a connectivity service¶
Use the following REST RPC to invoke TAPI module in order to delete a given optical connectivity service.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-connectivity:delete-connectivity-service
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-connectivity:input": {
"tapi-connectivity:service-id-or-name": "<Service_UUID_or_Name>"
}
}
Note
Deleting OTN connectivity services implies proceeding in the reverse way to their creation. Thus, OTN connectivity service deletion must respect the three following steps: 1. delete first all 10GE services supported over any ODU4 to be deleted 2. delete ODU4 3. delete MC-OTSi supporting the just deleted ODU4
T-API Notification Service¶
RPC calls implemented:
create-notification-subscription-service
get-supported-notification-types
delete-notification-subscription-service
get-notification-subscription-service-details
get-notification-subscription-service-list
get-notification-list
Sulfur SR1 extends the T-API interface support by implementing the T-API notification service. This feature allows TransportPCE to write and read tapi-notifications stored in topics of a Kafka server. It also upgrades the nbinotifications module to support the serialization and deserialization of tapi-notifications into JSON format and vice-versa. Current implementation of the notification service creates a Kafka topic and stores tapi-notification on reception of a create-notification-subscription-service request. Only connectivity-service related notifications are stored in the Kafka server.
In comparison with openroadm notifications, in which several pre-defined kafka topics are created on nbinotification module instantiation, tapi-related kafka topics are created on-demand. Upon reception of a create-notification-subscription-service request, a new topic will be created in the Kafka server. This topic is named after the connectivity-service UUID.
Note
Creating a Notification Subscription Service could include a list of T-API object UUIDs, therefore 1 topic per UUID is created in the Kafka server.
In the current implementation, only Connectivity Service related notification are supported.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-notification:get-supported-notification-types
The response body will include the type of notifications supported and the object types
Use the following RPC to create a Notification Subscription Service.
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-notification:create-notification-subscription-service
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-notification:input": {
"tapi-notification:subscription-filter": {
"tapi-notification:requested-notification-types": [
"ALARM_EVENT"
],
"tapi-notification:requested-object-types": [
"CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE"
],
"tapi-notification:requested-layer-protocols": [
"<LAYER_PROTOCOL_NAME>"
],
"tapi-notification:requested-object-identifier": [
"<Service_UUID>"
],
"tapi-notification:include-content": true,
"tapi-notification:local-id": "localId",
"tapi-notification:name": [
{
"tapi-notification:value-name": "Subscription name",
"tapi-notification:value": "<notification_service_name>"
}
]
},
"tapi-notification:subscription-state": "ACTIVE"
}
}
This call will return the UUID of the Notification Subscription service, which can later be used to retrieve the details of the created subscription, to delete the subscription (and all the related kafka topics) or to retrieve all the tapi notifications related to that subscription service.
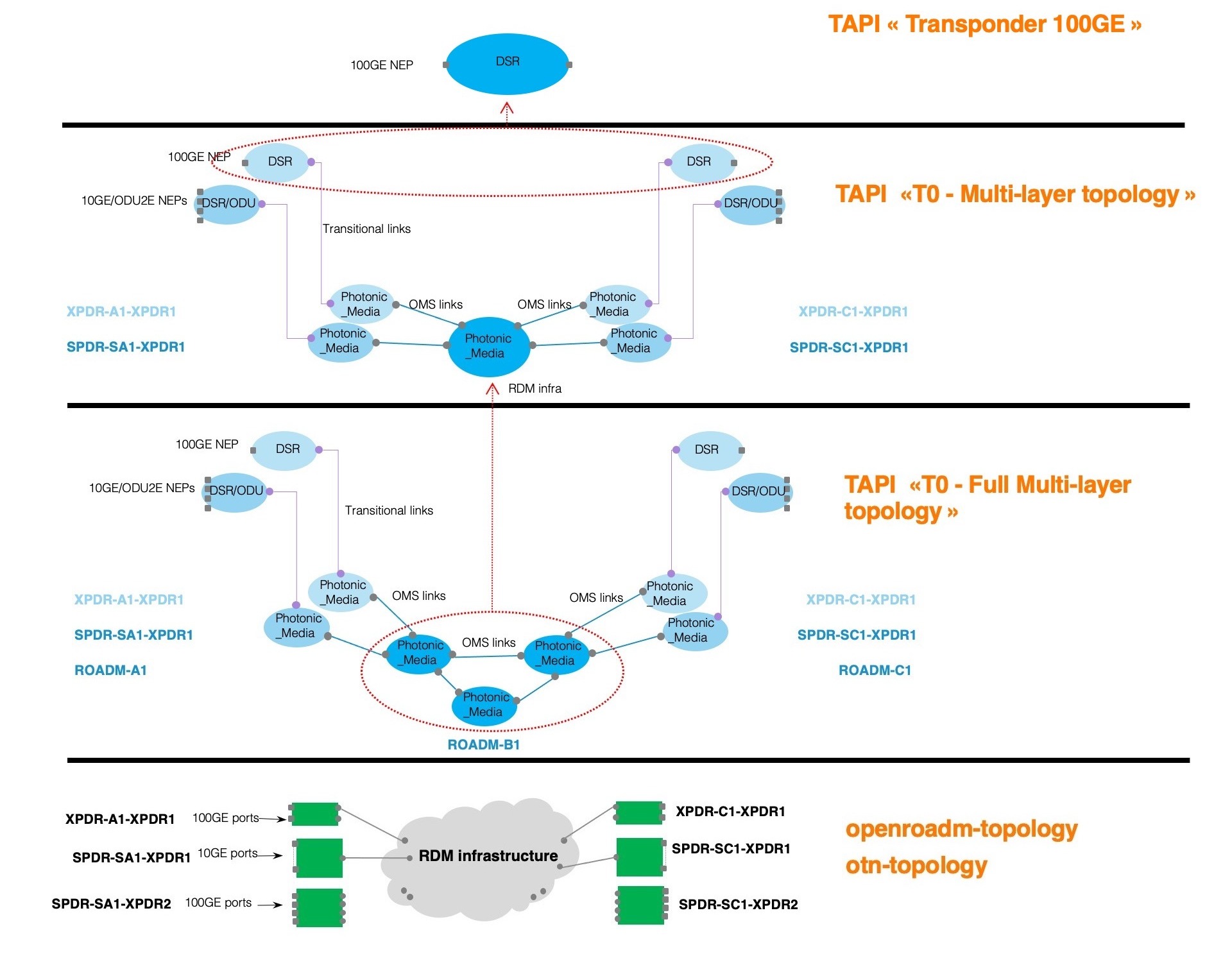
The figure below shows an example of the application of tapi and nbinotifications in order to notify when there is a connectivity service creation process. Depending on the status of the process a tapi-notification with the corresponding updated state of the connectivity service is sent to the topic “Service_UUID”.
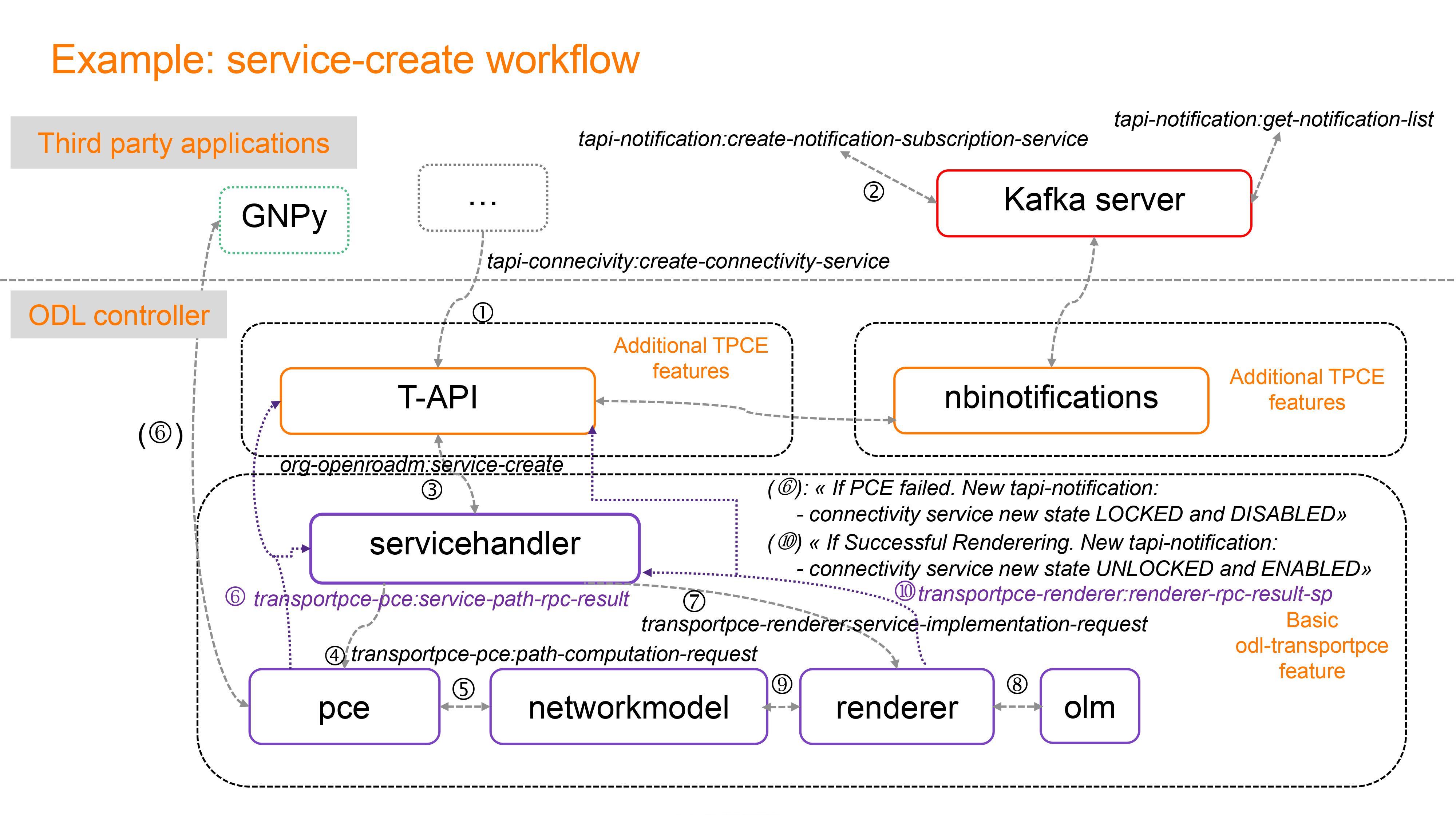
Additionally, when a connectivity service breaks down or is restored a tapi notification alarming the new status will be sent to a Kafka Server. Below an example of a tapi notification is shown.
Sample JSON T-API notification
{
"nbi-notifications:notification-tapi-service": {
"layer-protocol-name": "<LAYER_PROTOCOL_NAME>",
"notification-type": "ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_CHANGE",
"changed-attributes": [
{
"value-name": "administrativeState",
"old-value": "<LOCKED_OR_UNLOCKED>",
"new-value": "<UNLOCKED_OR_LOCKED>"
},
{
"value-name": "operationalState",
"old-value": "DISABLED_OR_ENABLED",
"new-value": "ENABLED_OR_DISABLED"
}
],
"target-object-name": [
{
"value-name": "Connectivity Service Name",
"value": "<SERVICE_UUID>"
}
],
"uuid": "<NOTIFICATION_UUID>",
"target-object-type": "CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE",
"event-time-stamp": "2022-04-06T09:06:01+00:00",
"target-object-identifier": "<SERVICE_UUID>"
}
}
To retrieve these tapi connectivity service notifications stored in the kafka server:
REST API : POST /rests/operations/tapi-notification:get-notification-list
Sample JSON Data
{
"tapi-notification:input": {
"tapi-notification:subscription-id-or-name": "<SUBSCRIPTION_UUID_OR_NAME>",
"tapi-notification:time-period": "time-period"
}
}
Further development will support more types of T-API objects, i.e., node, link, topology, connection…
odl-transportpce-dmaap-client¶
This feature allows TransportPCE application to send notifications on ONAP Dmaap Message router following service request results. This feature listens on NBI notifications and sends the PublishNotificationService content to Dmaap on the topic “unauthenticated. TPCE” through a POST request on /events/unauthenticated.TPCE It uses Jackson to serialize the notification to JSON and jersey client to send the POST request.
odl-transportpce-nbinotifications¶
This feature allows TransportPCE application to write and read notifications stored in topics of a Kafka server. It is basically composed of two kinds of elements. First are the ‘publishers’ that are in charge of sending a notification to a Kafka server. To protect and only allow specific classes to send notifications, each publisher is dedicated to an authorized class. There are the ‘subscribers’ that are in charge of reading notifications from a Kafka server. So when the feature is called to write notification to a Kafka server, it will serialize the notification into JSON format and then will publish it in a topic of the server via a publisher. And when the feature is called to read notifications from a Kafka server, it will retrieve it from the topic of the server via a subscriber and will deserialize it.
For now, when the REST RPC service-create is called to create a bidirectional end-to-end service, depending on the success or the fail of the creation, the feature will notify the result of the creation to a Kafka server. The topics that store these notifications are named after the connection type (service, infrastructure, roadm-line). For instance, if the RPC service-create is called to create an infrastructure connection, the service notifications related to this connection will be stored in the topic ‘infrastructure’.
The figure below shows an example of the application nbinotifications in order to notify the progress of a service creation.
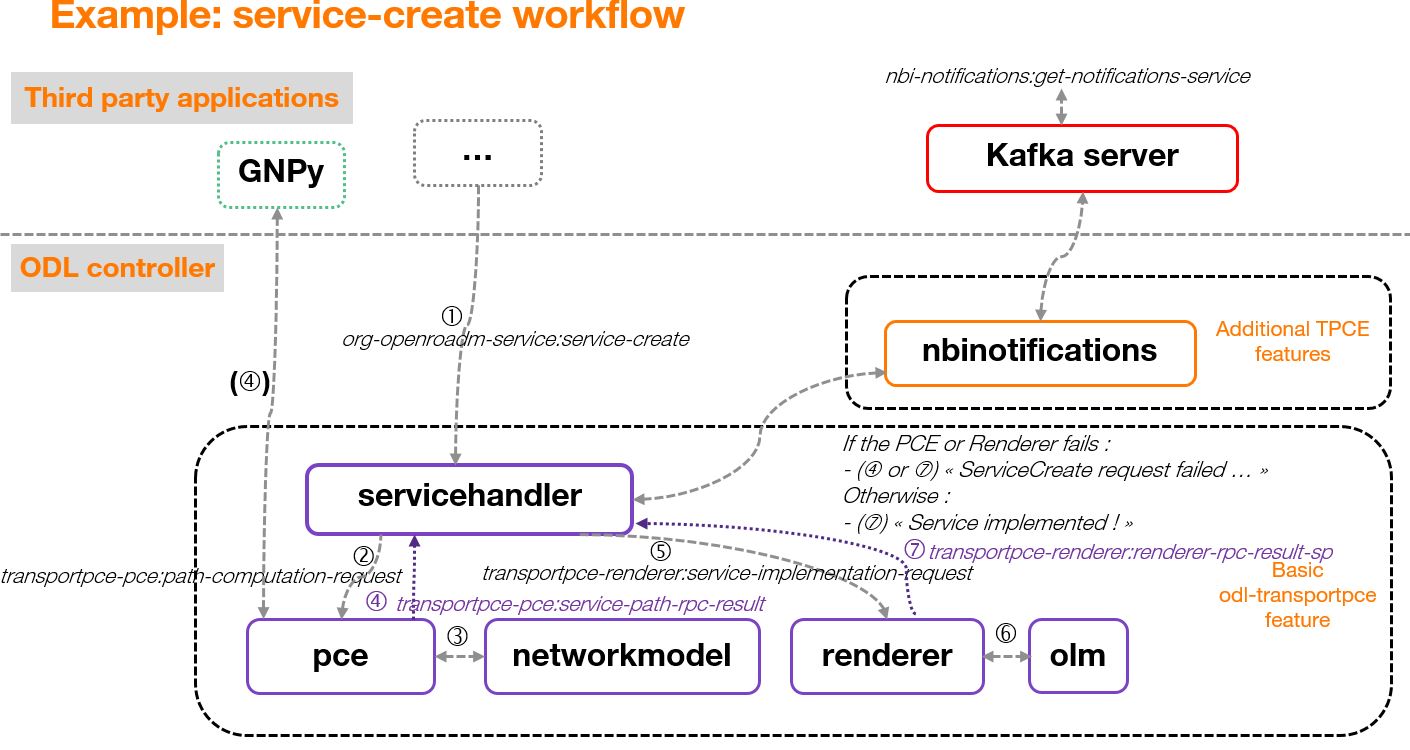
Depending on the status of the service creation, two kinds of notifications can be published to the topic ‘service’ of the Kafka server.
If the service was correctly implemented, the following notification will be published :
Service implemented ! : Indicates that the service was successfully implemented. It also contains all information concerning the new service.
Otherwise, this notification will be published :
ServiceCreate failed … : Indicates that the process of service-create failed, and also contains the failure cause.
To retrieve these service notifications stored in the Kafka server :
REST API : POST /rests/operations/nbi-notifications:get-notifications-process-service
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"connection-type": "service",
"id-consumer": "consumer",
"group-id": "test"
}
}
Note
The field ‘connection-type’ corresponds to the topic that stores the notifications.
Another implementation of the notifications allows to notify any modification of operational state made about a service. So when a service breaks down or is restored, a notification alarming the new status will be sent to a Kafka Server. The topics that store these notifications in the Kafka server are also named after the connection type (service, infrastructure, roadm-line) accompanied of the string ‘alarm’.
To retrieve these alarm notifications stored in the Kafka server :
REST API : POST /rests/operations/nbi-notifications:get-notifications-alarm-service
Sample JSON Data
{
"input": {
"connection-type": "infrastructure",
"id-consumer": "consumer",
"group-id": "test"
}
}
Note
This sample is used to retrieve all the alarm notifications related to infrastructure services.